For an inventory for our company related to remediation (anything that was deployed before using the portal we import it via terraform and later apply our standards too) we have been asked to get details about each virtual network and subnet and the connected ressources to those vnet ,why ? because sometimes we will need to add some routes in our udr , sometimes we update the nsgs and some other times if we found out a vnet is a legacy we see if we are going to delete it .
In an earlier blog post we have written : PowerShell Automation for Azure Networks: Detailed VNET and Subnet Analysis we have extracted everything related to all the vent in our
subscriptions (over 100 sub) for that my college asked me if it is possible to write another script only to target one vnet or one subnet in a vnet ,and that’s normal since he does not need details about all the vnet’s that exist , and he need an updated version of the report since any change can happen and he can no be based on an older report .
for that I have added this two scripts below to help extract details about the vnet and subent and save the report in a stylish table format in excel .
How to Use :
1 – Connect to Azure: Run Connect-AzAccount to authenticate and connect to your Azure account.
2- Install-Module -Name ImportExcel -Scope CurrentUser -Force
3- Insert the subscription id ,the ressource group name ,the vnet ,and the subnet is optionel.
4 – Execute the Script: Copy and run the script in your PowerShell environment.
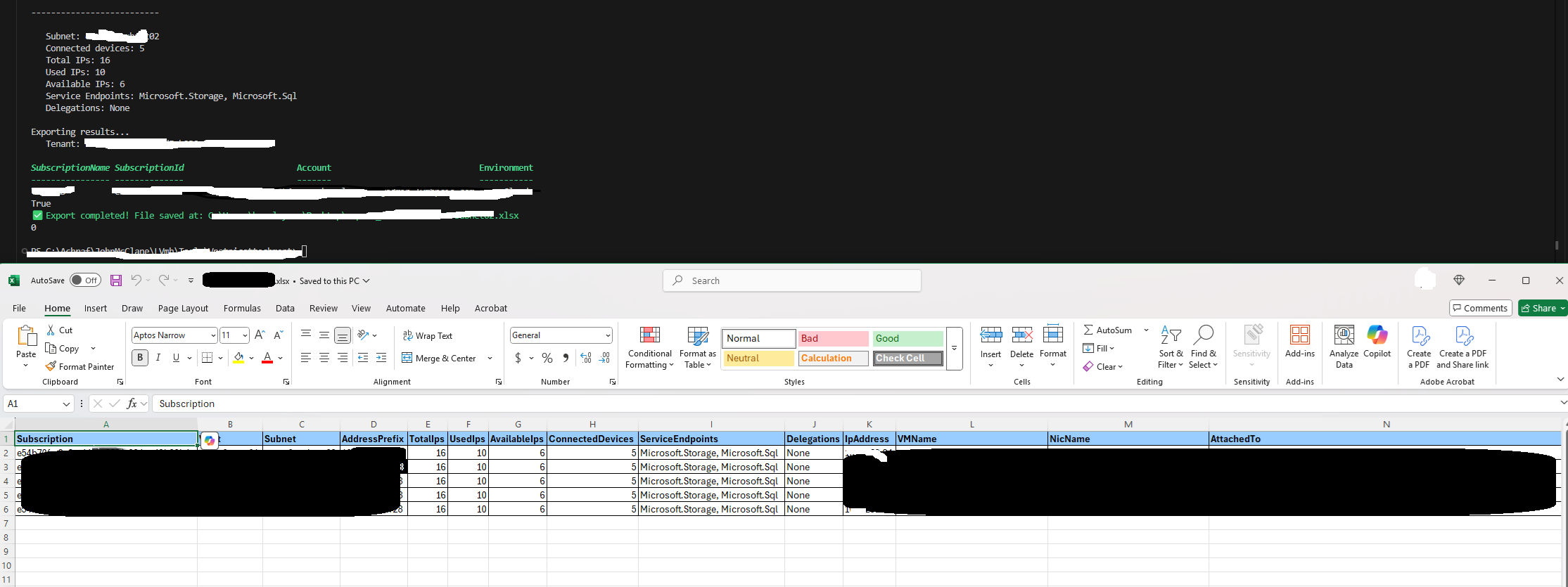
5 – View Results: The script outputs a summary to the console and saves detailed results to a specified Excel file.
6 – Access the Excel : Open the XlSX file located at path.xlxs` to review the details.
This script is useful for administrators needing to audit network configurations and IP usage across multiple Azure subscriptions.
Script:
$subscriptionId = ''
$resourceGroupName = ''
$vnetName = ''
$subnetName = '' # Can be empty to process all subnets
$desktopPath = [System.Environment]::GetFolderPath("Desktop")
$exportDirectory = "$desktopPath\export_subnets"
Import-Module ImportExcel -Force
# Connect to Azure
Select-AzSubscription -SubscriptionId $subscriptionId
# Get the virtual network
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name $vnetName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName
if (-not $vnet) {
Write-Host "The VNet $vnetName was not found." -ForegroundColor Red
exit
}
# Function to process a single subnet
function Process-Subnet {
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
$subnet
)
Write-Host "--------------------------"
Write-Host " "
Write-Host " Subnet: $($subnet.Name)"
$connectedDevices = $subnet.IpConfigurations.Count
Write-Host " Connected devices: $connectedDevices"
# Calculate IPs
$subnetMask = $subnet.AddressPrefix.Split('/')[1]
$totalIps = [math]::Pow(2, 32 - $subnetMask)
$reservedIps = 5
$usedIps = $connectedDevices + $reservedIps
$availableIps = $totalIps - $usedIps
Write-Host " Total IPs: $totalIps"
Write-Host " Used IPs: $usedIps"
Write-Host " Available IPs: $availableIps"
# Service Endpoints and Delegations
$serviceEndpoints = if ($subnet.ServiceEndpoints) { $subnet.ServiceEndpoints.Service -join ', ' } else { "None" }
Write-Host " Service Endpoints: $serviceEndpoints"
$delegations = if ($subnet.Delegations) { $subnet.Delegations.ServiceName -join ', ' } else { "None" }
Write-Host " Delegations: $delegations"
# Subnet address
$addressPrefixString = $subnet.AddressPrefix -join ', '
# Network interfaces
$networkInterfaces = Get-AzNetworkInterface | Where-Object { $_.IpConfigurations.Subnet.Id -eq $subnet.Id }
$results = @()
foreach ($nic in $networkInterfaces) {
foreach ($ipConfig in $nic.IpConfigurations) {
$vm = Get-AzVM | Where-Object { $_.Id -eq $nic.VirtualMachine.Id }
$vmName = if ($vm) { $vm.Name } else { "Not Available" }
$results += [PSCustomObject]@{
Subscription = [string]$subscriptionId
VNet = [string]$vnetName
Subnet = [string]$subnet.Name
AddressPrefix = [string]$addressPrefixString
TotalIps = [int64]$totalIps
UsedIps = [int64]$usedIps
AvailableIps = [int64]$availableIps
ConnectedDevices= [int]$connectedDevices
ServiceEndpoints= [string]$serviceEndpoints
Delegations = [string]$delegations
IpAddress = [string]$ipConfig.PrivateIpAddress
VMName = [string]$vmName
NicName = [string]$nic.Name
AttachedTo = [string]"NIC: $($nic.Name), VM: $vmName"
}
}
}
# If no device found, add an empty row
if ($results.Count -eq 0) {
$results += [PSCustomObject]@{
Subscription = [string]$subscriptionId
VNet = [string]$vnetName
Subnet = [string]$subnet.Name
AddressPrefix = [string]$addressPrefixString
TotalIPs = [int64]$totalIps
UsedIPs = [int64]$usedIps
AvailableIPs = [int64]$availableIps
ConnectedDevices= [int]0
ServiceEndpoints= [string]$serviceEndpoints
Delegations = [string]$delegations
IpAddress = [string]""
VMName = [string]""
NicName = [string]""
AttachedTo = [string]"Not Applicable"
}
}
return $results
}
# Determine which subnets to process
$subnetsToProcess = @()
if ([string]::IsNullOrEmpty($subnetName)) {
$subnetsToProcess = $vnet.Subnets
$exportFileName = "all_subnets.xlsx"
} else {
$subnet = $vnet.Subnets | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq $subnetName }
if (-not $subnet) {
Write-Host "The subnet $subnetName was not found." -ForegroundColor Red
exit
}
$subnetsToProcess = @($subnet)
$exportFileName = "$subnetName.xlsx"
}
# Process all selected subnets
$allResults = @()
foreach ($subnet in $subnetsToProcess) {
$results = Process-Subnet -subnet $subnet
$allResults += $results
}
# Create export directory if it doesn't exist
if (-not (Test-Path -Path $exportDirectory)) {
Write-Host "Creating export directory: $exportDirectory"
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $exportDirectory | Out-Null
}
$excelFilePath = "$exportDirectory\$exportFileName"
try {
$excelApp = New-Object -ComObject Excel.Application
$excelApp.Visible = $false
$workbook = $excelApp.Workbooks.Add()
$worksheet = $workbook.Sheets.Item(1)
$worksheet.Name = "Subnet Report"
# Define headers with formatting
$headers = @("Subscription", "VNet", "Subnet", "AddressPrefix", "TotalIPs", "UsedIPs", "AvailableIPs",
"ConnectedDevices", "ServiceEndpoints", "Delegations", "IpAddress", "VMName", "NicName", "AttachedTo")
for ($i = 0; $i -lt $headers.Count; $i++) {
$cell = $worksheet.Cells.Item(1, $i + 1)
$cell.Value = $headers[$i]
$cell.Font.Bold = $true
$cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 37
$cell.Borders.LineStyle = 1
}
# Insert data with borders
$row = 2
foreach ($result in $allResults) {
for ($col = 1; $col -le $headers.Count; $col++) {
$cell = $worksheet.Cells.Item($row, $col)
$propertyName = $headers[$col - 1]
$propertyValue = $result.$propertyName
# Convert numeric values to strings for Excel
if ($propertyValue -is [int64] -or $propertyValue -is [int] -or $propertyValue -is [double]) {
$cell.Value2 = [double]$propertyValue
} else {
$cell.Value2 = [string]$propertyValue
}
$cell.Borders.LineStyle = 1
}
$row++
}
# Auto-fit column widths
$worksheet.Columns.AutoFit()
# Save and close the Excel file
$workbook.SaveAs($excelFilePath)
$workbook.Close()
$excelApp.Quit()
Write-Host "✅ Export completed! File saved at: $excelFilePath" -ForegroundColor Green
Invoke-Item -Path $excelFilePath
} catch {
Write-Host "❌ An error occurred: $($_.Exception.Message)" -ForegroundColor Red
} finally {
if ($excelApp) { [System.Runtime.Interopservices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($excelApp) }
}
Ps : This article was written in collaboration with my friend Malik .